|
Number & Operations for Teachers Copyright David & Cynthia Thomas, 2009 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
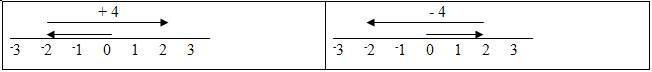
Measurement Model Corresponding
measurement models for the operations -2 + 4 = 2 and
2
4 = -2 are
shown in Figure 2.7. In both
operations, an arrow with its tail at the origin points to the first term in
the expression. The second term is
represented by an arrow arranged head-to-tail with the first. The head of the second arrow is positioned
over the indicated sum or difference.
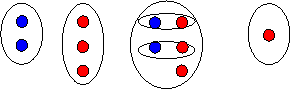
Figure 2.7: Measurement models for -2 + 4 = 2 and 2 4 = -2 In order to accommodate addition and subtraction of both positive and negative numbers, the following conventions are used in the measurement model. · To add a positive, face right and step forward (i.e., to the right) along the number line · To subtract a positive, face left and step forward (i.e., to the left) along the number line · To add a negative, face right and step backward (i.e., to the left) along the number line · To subtract a negative, face left and step backward (i.e., to the right) along the number line Example 2.1 Using both a set model and a measurement model, represent the operation 2 -2 = 4.
Example 2.2 Using both a set model and a measurement model, represent the operation 2 + -3 = -1. Solution 2.2
Fact families for addition and subtraction of integers are similar to those
for addition and subtraction of whole numbers. Both operations are closed on the set of
integers.
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|