|
Number & Operations for Teachers Copyright David & Cynthia Thomas, 2009 |
||||
|
Understanding the
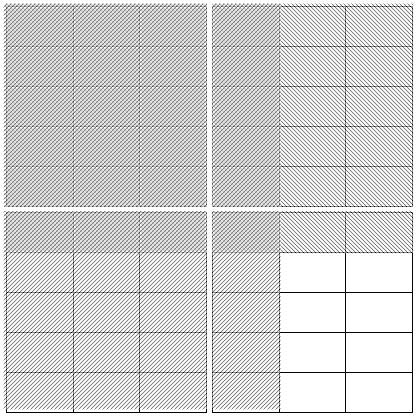
Standard Fraction Multiplication Algorithm In general, the area model for the product of two fractions, a/b x c/d, represents the solution as ac cells, each having an area of 1/bd of a unit square. In this representation, the product bd may be viewed as a common denominator for the two given fractions and the fraction 1/bd as a common divisor. In the case of the product 6/5 x 4/3 , the algebraic expression 1/bd corresponds to the fraction 1/(3×5) = 1/15 and the algebraic expression ac corresponds to the product 6×4 = 24. This product is modeled in Figure 5.6, where the answer is identified as the fraction 24/15, or 24 cells each with area 1/15. Numeric representations of this sort may or may not be reduced to lowest terms. In the case of the fraction 24/15, further simplification is possible by collecting the overlapping cells into groups of three, each group equivalent to a row in the unit whole. These groups are then counted and the result “8 groups of 3 cells” is obtained. Because the unit square contains five such groups (ie.e, rows), each group of three constitutes one-fifth of the whole. Therefore, the result “8 groups of 3 cells” may be interpreted as representing eight-fifths of the whole (See Figure 5.7).
Figure 5.6: Area Model for Fraction Addition, 6/5 + 4/3
Figure 5.7: Simplification |
||||
|
|