Overview of Modern
Geometry
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
For whom was Modern Geometry
written?
Modern
Geometry was
written with a particular audience in mind: Undergraduate mathematics
education majors and practicing secondary school mathematics teachers. Audio |
|||
|
What
is Modern Geometry about? Modern
Geometry provides
a historically-grounded, applications-oriented, technology-rich survey of
Euclidean, transformation, hyperbolic, fractal, and projective geometry. Audio The
Modern Geometry textbook presents concepts, relationships, and procedures
in a systematic and deductive manner.
Audio Table of Contents
1 Geometry Through the Ages 11.1 Greek Geometry Before Euclid 2 1.2 Euclid and the Elements 10 1.3 Neutral Geometry 20 1.4 Famous Open Problems in Geometry 28 2 Topics in Euclidean Geometry 452.1 Elementary Constructions 47 2.2 Exploring Relationships Between Objects 59 2.3 Formal Geometric Proof 73 3 Other Geometries 833.1 The Concept of Parallelism 86 3.2 Points, Lines, and Curves in Poincare's Disc Model 93 3.3 Polygons in Hyperbolic Space 113 3.4 Congruence in Hyperbolic Space 123 4 Transformation Geometry 1294.1 An Analytic Model of the Euclidean Plane 130 4.2 Representing Linear Transformations in 2-space with Matrices 143 4.3 The Direct Isometries: Translations and Rotations 157 4.4 Indirect Isometries: Reflections 171 4.5 Composition and Analysis of Transformations 179 4.6 Other Linear Transformations 189 5 Fractal Geometry 2035.1 Introduction to Self-similarity 206 5.2 Fractal Dimension 219 5.3 Iterated Function Systems 235 5.4 From Order to Chaos 245 5.5 The Mandelbrot Set 257 6 Projective Geometry 2696.1 Elements of Perspective Drawing 269 6.2 Introduction to Projective Geometry 283 6.3 The Cross Ratio 299 6.4 Applications of the Cross Ratio 313 6.5 Matrix Methods for 3-point Perspective Transformations 319 6.6 Applications of Geometry in Remote Sensing 329 6.7 Applications of Geometry in Terrain Rendering 337 |
|||
How are the Technology
Resources used?
Using
mathematical modeling tools such as the Geometers Sketchpad, NonEuclid,
and MSW Logo, image processing tools such as Scion Image, and
WWW-based information resources such as Euclid's
Elements, students explore and extend concepts, skills, and
relationships presented in the text. Audio The
Technology Resources include over 100 interactive activities for
extending and applying concepts and procedures developed in the
textbook. For instance ... Audio
|
|||
|
How
do the technology-based activities relate to the content and format of the
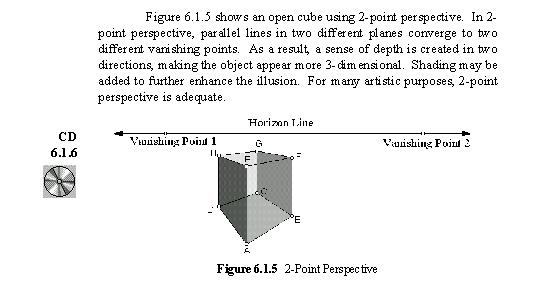
textbook? 1.
Where the textbook uses a figure to illustrate the concept of a
two-point perspective view of a cube ...
Audio
|
|||
|
The Technology Resources provide an
interactive Geometers Sketchpad sketch or
JavaSketchpad applet to explore
the range of perspectives possible in such a view. Audio |
|||
|
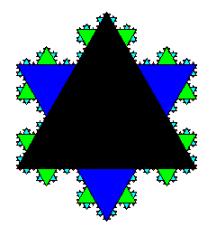
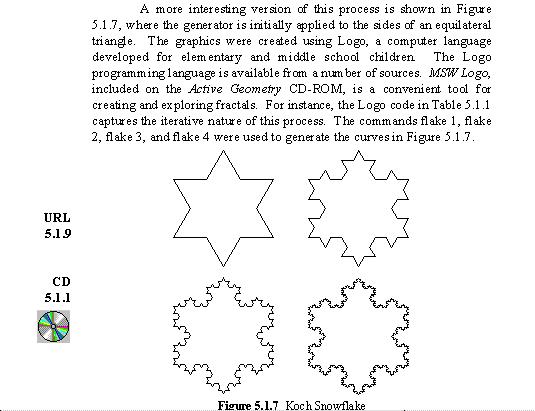
2.
Where the textbook uses a figure to illustrate the concept of a
fractal curve ... Audio
|
|||
|
The Technology Resources provide an
interactive MSW Logo model for
generating different approximations to the curve. Audio |
|||
|
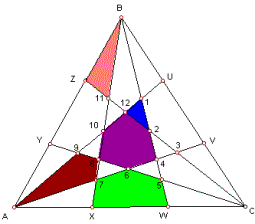
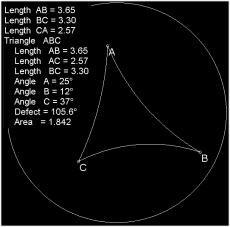
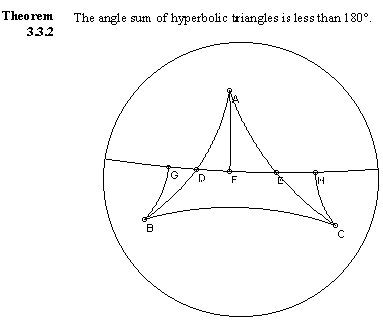
3.
Where the
textbook uses a figure to represent the features of triangles in hyperbolic
space ... Audio
|
|||
|
The Technology Resources provide an
interactive model of hyperbolic space called
NonEuclid in which students may create and measure triangles
themselves. Audio |
|||
|
4.
Where the
textbook uses a figure to illustrate data visualization … Audio
|
|||
|
The
Technology Resources provide an interactive terrain model using dem3D. Audio |
|||
|
5.
Where the textbook provides a historical reference for the life and
achievements of the mathematician Henri Poincare ... Audio
|
|||
|
The Technology Resources provide a link
to Poincare’s biography in the MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. Audio |
|||
Why should technology play any
role in the preparation and continuing education of geometry teachers?
1.
The Modern Geometry Technology Resources have been
provided because of my strong belief that having convenient access to
modeling tools and information resources such as these empowers students to
think, act, and communicate mathematically in new and powerful ways. Audio |
|||
|
2.
Modern Geometry was written to empower undergraduate mathematics education majors in
this manner and to encourage teachers of mathematics to make similar
opportunities available to their own students. Audio |
|||
|
3.
My hope is that Modern Geometry will inspire you and your
students to undertake voyages of mathematical discovery facilitated by these
technologies. Bon voyage! Audio |
|
|
COPYRIGHT © 2002 by Brooks/Cole Publishing Company A division of International
Thompson Publishing, Inc. |